How does eXciteOSA work?
The world’s first clinically proven daytime therapy for mild obstructive sleep apnea & primary snoring
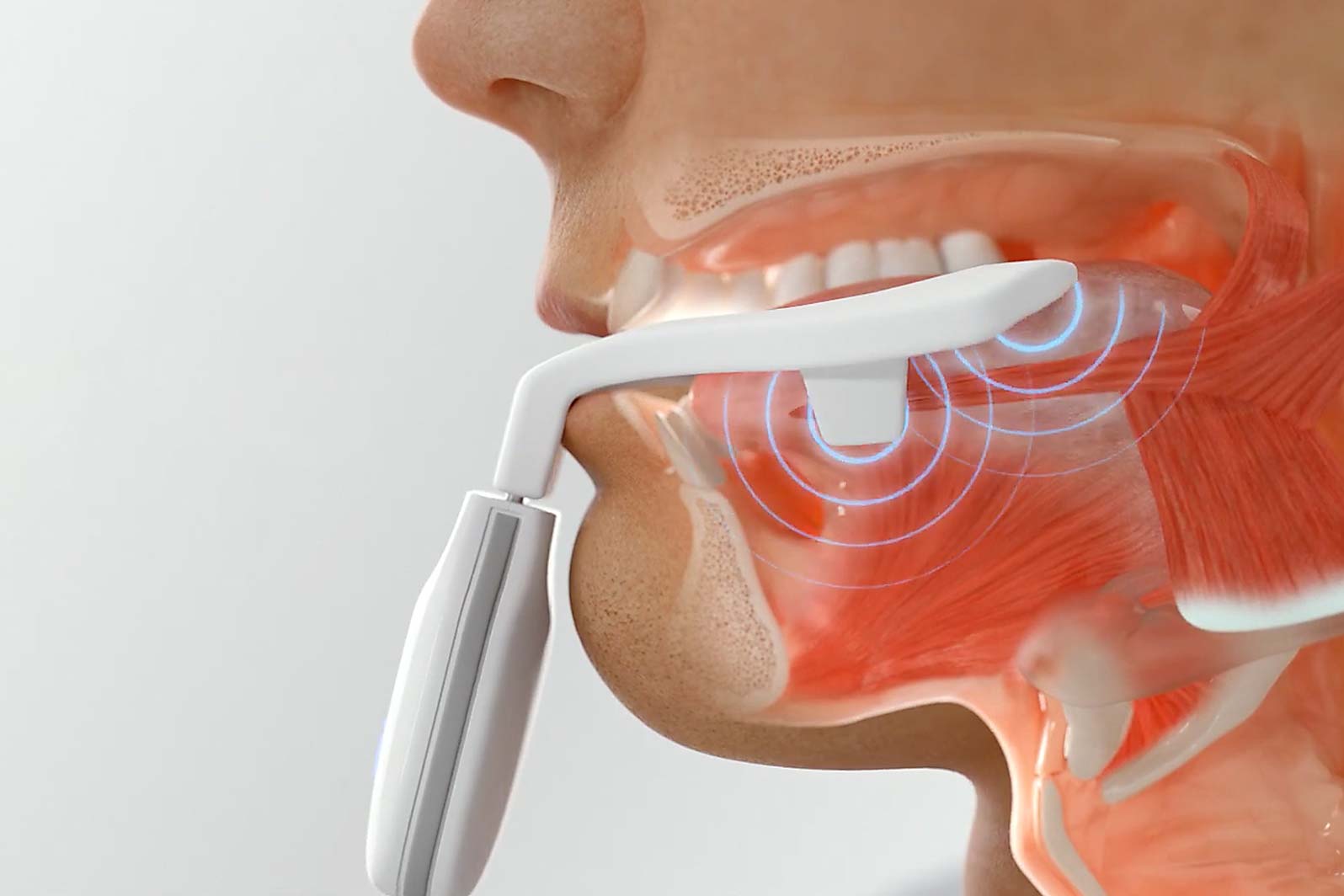
Reduced tongue endurance: a common root cause of OSA
Apneas and hypopneas are caused by collapse of the upper airway. Studies have demonstrated that patients with OSA have reduced tongue muscle endurance. eXciteOSA promotes the endurance of the tongue muscles to prevent the collapse of the upper airway during sleep3.
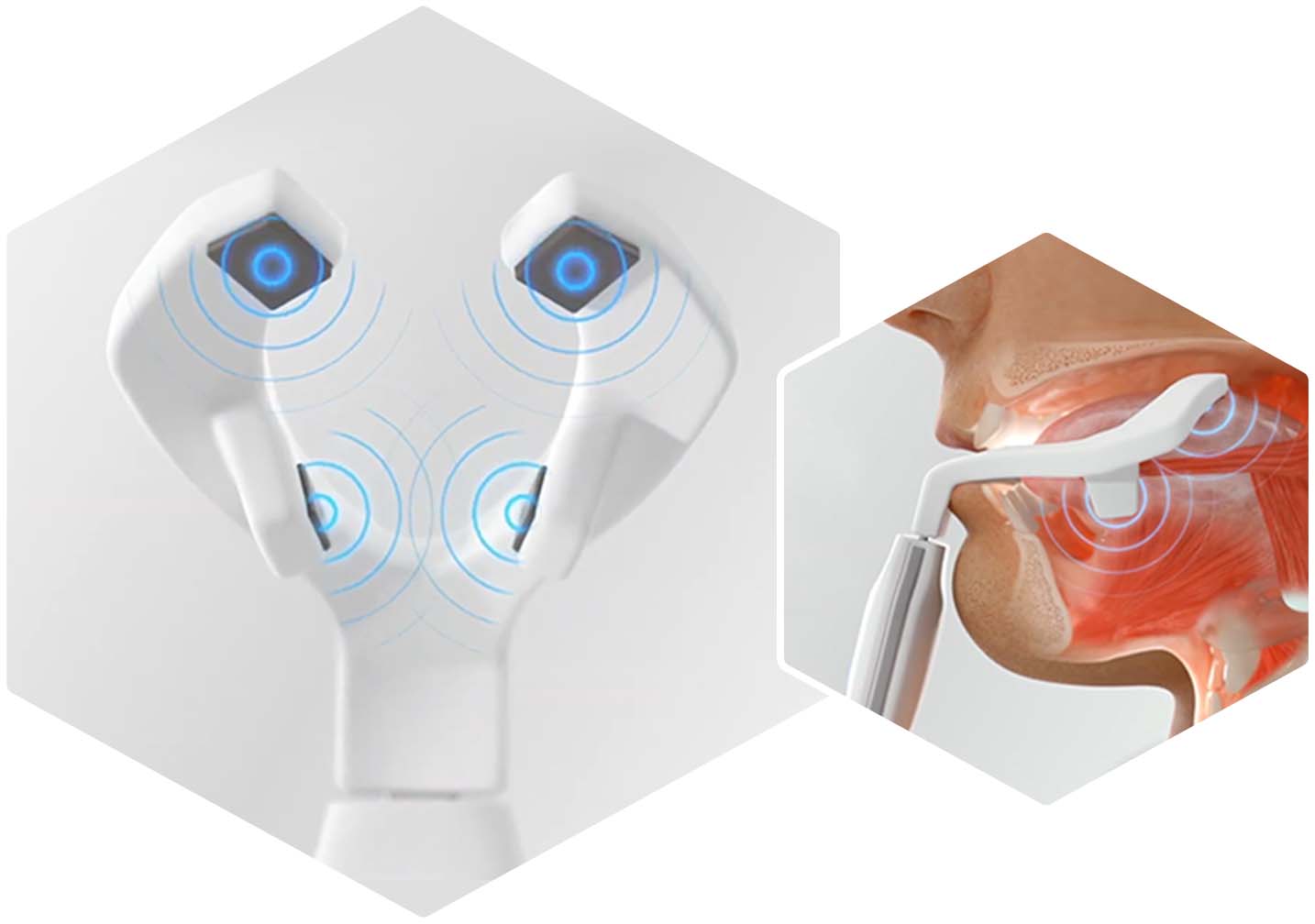
Targeted therapy
eXciteOSA delivers targeted Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES) to tone the upper airway muscles and tongue to prevent them from collapsing in the airway3.
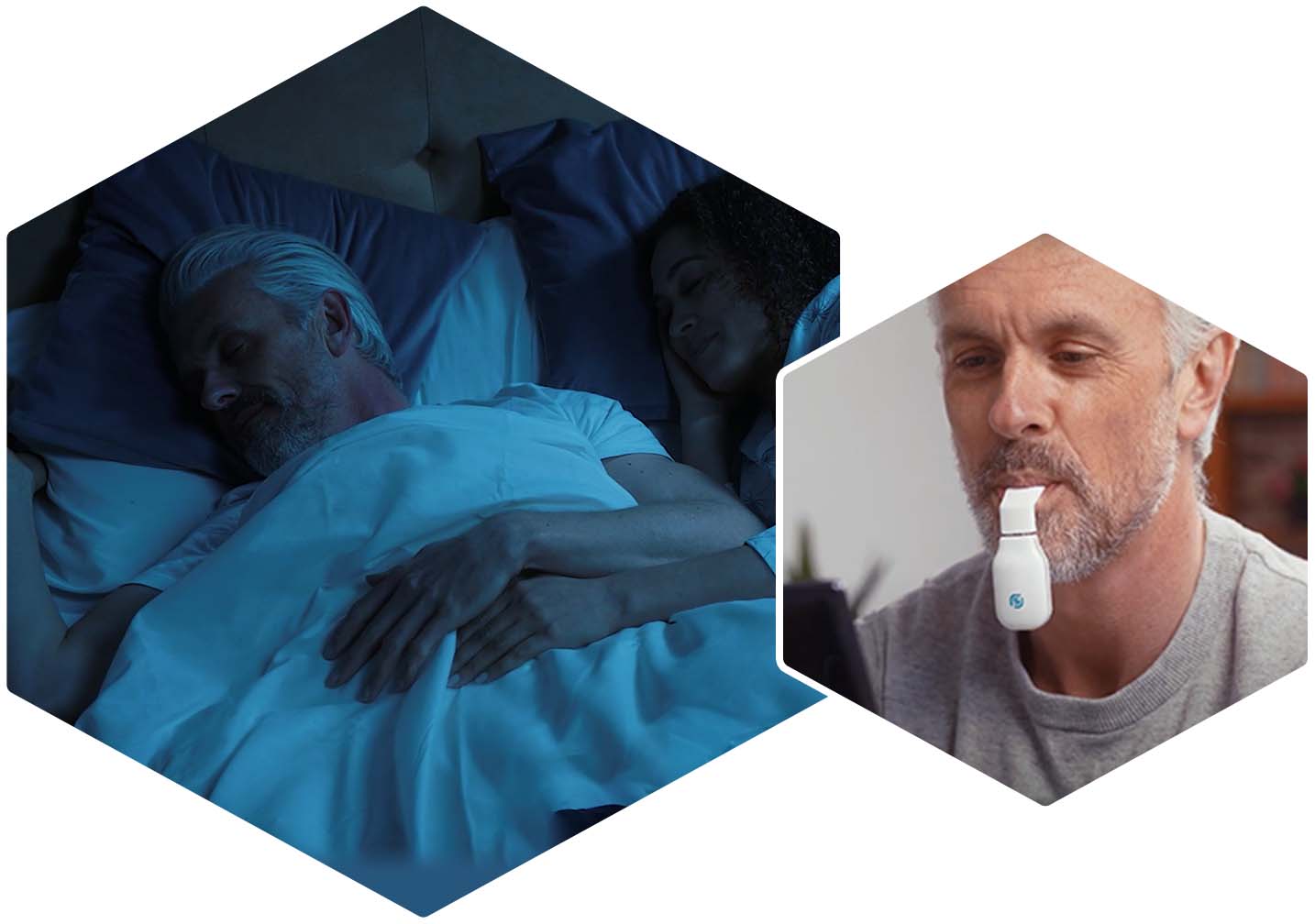

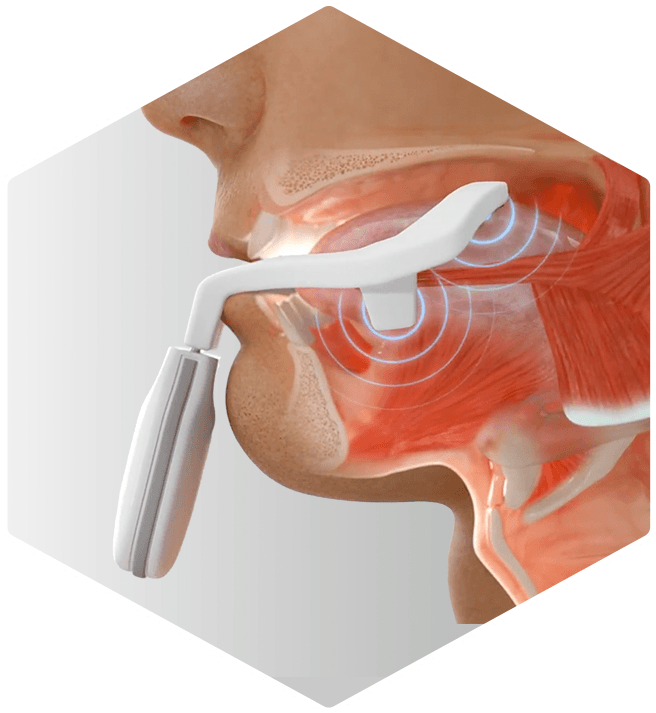
Free the airway
Reduce sleep apnea severity with the world’s first clinically proven daytime therapy used during the day for night-time results. Therapy with eXciteOSA is associated with increased tongue muscle endurance, improved mild sleep obstructive apnea and improved quality of sleep1-3.
The science
NMES applied to the tongue: a new, FDA-cleared and patient-friendly daytime therapy helping to treat a common root cause of mild obstructive sleep apnea and snoring.
Combining two established concepts has led to a revolutionary daytime therapy
1. The tongue
Research has shown that individuals with OSA have impaired genioglossus (tongue) endurance compared to those without OSA6.
2. NMES
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) of skeletal muscles is associated with an improvement of muscle endurance4-5.
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) machines stimulates the sensory nerves (the nerves that send signals from the body to the brain) with the purpose of disrupting the pain signal.
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) also uses electrical stimulation, but targets the motor nerves (the nerves that send signals from the brain to the body) in order to stimulate the muscles directly.
Sensory and motor nerves fire at different frequencies, which is how TENS and NMES devices are able to impact them differently.
eXciteOSA® is a user-controllable neuromuscular electrical stimulator (NMES) that delivers a mild electrical current with defined frequencies to stimulate and improve muscle function in the mouth and tongue.
Unlike traditional sleep apnea treatments, eXciteOSA® targets the tongue to promote endurance of the muscle, thereby reducing airway collapse and snoring during sleep.
A daytime therapy with no night-time wearable necessary for a better night’s sleep.
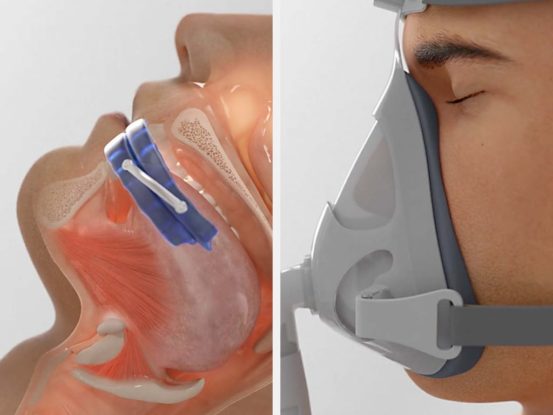
There are several options for treating sleep apnea.
Manudibular advancement devices (MADs) work by temporarily moving the jaw forward, in order to create more space in the airway.
CPAP delivers air pressure through a mask to open up the airway.
Surgery is usually an option to consider after other treatments have failed. Examples include removal of soft tissues from the airway, or procedures designed to stiffen the airway.
NMES physiologically retrains the upper airway and tongue to maintain the tongue’s natural position while you sleep, effectively helping your body help itself. eXciteOSA for sleep apnea is the only device that delivers NMES.
 NMES (eXciteOSA®) |
 MAD / CPAP |
 SURGERY |
|
| Treats a root cause of snoring |
|
|
|
| Nothing to wear at night |
|
|
|
| Evidence based |
|
|
|
| Low cost trial period |
|
|
|
| Helps your body to help itself |
|
|
|
Using eXciteOSA
Its quick, easy, comfortable and it works

Sits on the tongue
Once a day the medical grade silicone mouthpiece is placed in the mouth to sit around the tongue.
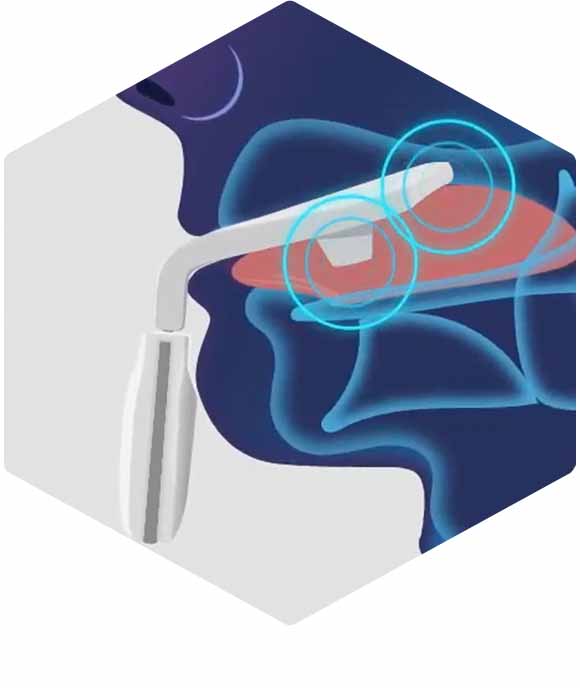
NMES therapy
During the 20-minute therapy session, gentle electrical pulses stimulate the tongue to improve muscle endurance.

Sleep freely
The result, after the initial 6-weeks, is a “retrained” tongue that holds its position at night, letting you sleep soundly.
Backed by evidence
Multiple studies have been conducted with over 140 patients and more are on the way.
References
- Baptista PM, Martinez Ruiz de Apodaca P, Carrasco M, Fernandez S, Wong PY, Zhang H, Hassaan A, Kotecha B. Daytime neuromuscular electrical therapy of tongue muscles in improving snoring in individuals with primary snoring and mild obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin Med 10(9):1-11 (2021).
- Nokes B, Baptista PM, Martínez Ruiz de Apodaca P, Carrasco-Llatas M, Fernandez S, Kotecha B, Wong PY, Zhang H, Hassaan A, Malhotra A. Transoral awake state neuromuscular stimulation therapy for mild obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep & Breathing (in-press; 2022).
- Nokes B, Schmickl CN, Brena R, Bosompra NN, Gilbertson D, Sands, SA, Bhattacharjee R, Mann DL, Ow ens RL, Malhotra A, Orr JE. The impact of daytime transoral neuromuscular stimulation on upper airway physiology in snoring and mild OSA. Physiological Reports (in-press; 2022).
- Nuhr M, Crevenna R, Gohlsch B, Bittner C, Pleiner J, Wiesinger G, Fialka-Moser V, Quittan M, Pette D. Functional and biochemical properties of chronically stimulated human skeletal muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 2003;89:202-208
- Gondin J, Brocca L, Bellinzona E, D’Antona G, Maffiuletti NA, Miotti D, Pellegrino MA, Bottinelli R. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation training induces atypical adaptations of the human skeletal muscle phenotype: a functional and proteomic analysis. J Appl Physiol 2011;110:433-450.
- Eckert DJ, Lo YL, Saboisky JP, Jordan AS, White DP, Malhotra A. Sensorimotor function of the upper-airway muscles and respiratory sensory processing in untreated obstructive sleep apnea. J Appl Physiol 2011;111(6):1644-1653.

